Introduction

Atmosphere's composition :
Dinitrogen N2 78%
Oxygen O2 20%
Argon Ar 9%
Carbon dioxyde CO2 0,40% *
Water vapor H2O 0-3%
Cox, Arthur N., éd. 2002. Allen’s Astrophysical Quantities. 4eéd. New York : Springer-Verlag. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-1186-0.
* "Vital signs: Carbon Dioxide". NASA Climate. May 2020. Retrieved 5 June 2020
Dinitrogen molecule
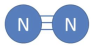
N2, the large amount of energy required to break the nitrogen-nitrogen triple bond makes this structure stable, which is why N2 is the most abundant in air.
Nitrogen reservoirs
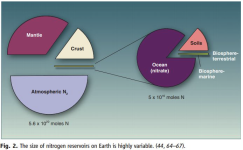
Canfield, Donald E., Alexander N. Glazer, et Paul G. Falkowski. 2010. « The Evolution and Future of Earth’s Nitrogen Cycle ». Science 330 (6001): 192‐96.
Nitrogen compounds
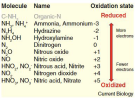
Ammonium NH4+
Nitrite NO2-
Nitrate NO3-
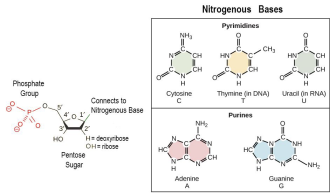
Why nitrogen is important to life ?
Hint : DNA
Medias
Impossible d'accéder à la ressource audio ou vidéo à l'adresse :
La ressource n'est plus disponible ou vous n'êtes pas autorisé à y accéder. Veuillez vérifier votre accès puis recharger le média.
Impossible d'accéder à la ressource audio ou vidéo à l'adresse :
La ressource n'est plus disponible ou vous n'êtes pas autorisé à y accéder. Veuillez vérifier votre accès puis recharger le média.