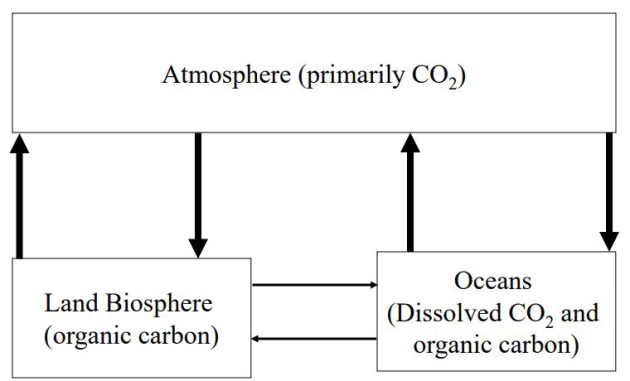
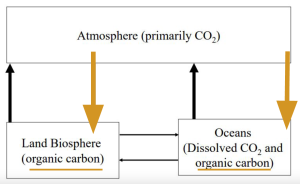
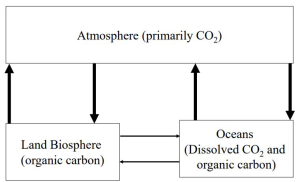
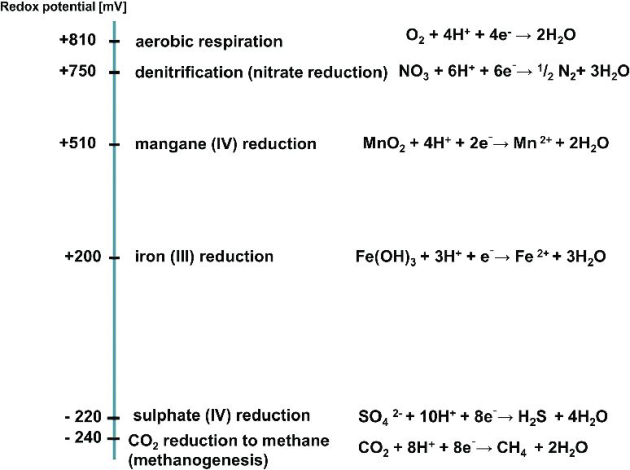
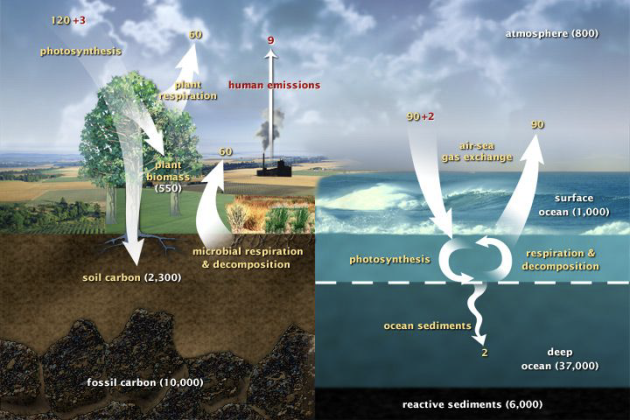
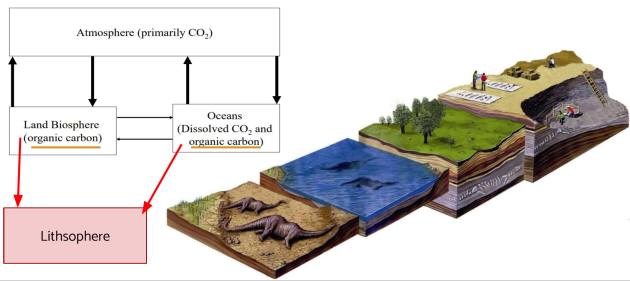
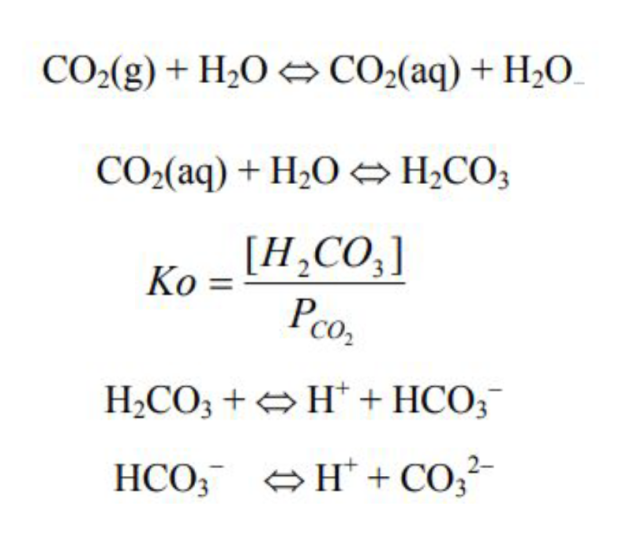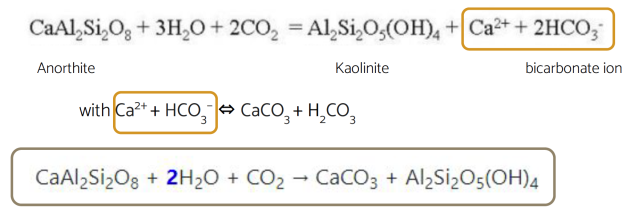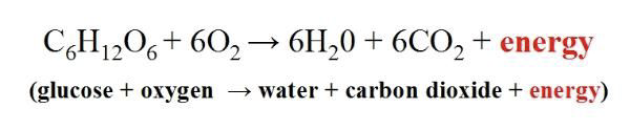Carbon cycle
Short cycle
Carbon cycle : Short cycle part 1
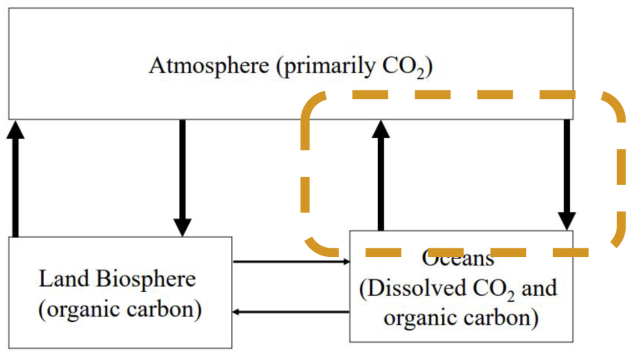
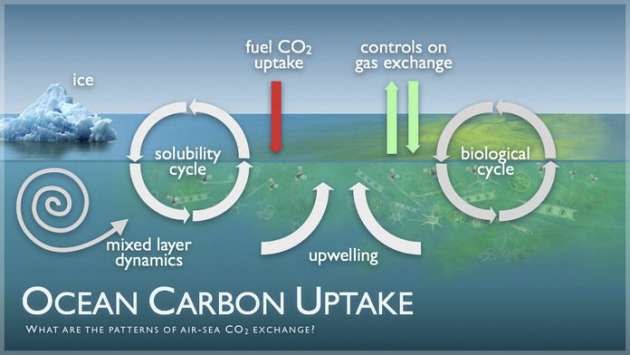
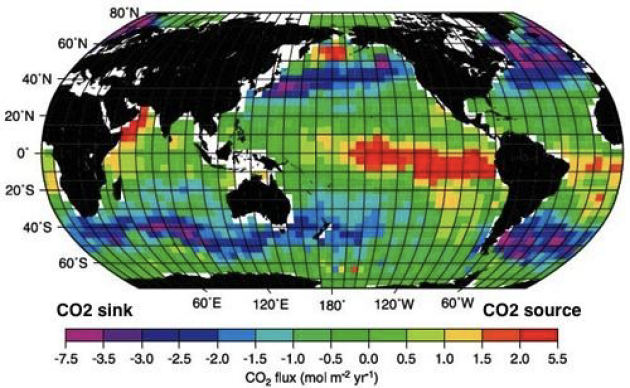
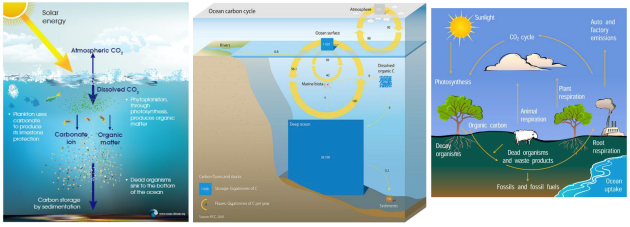
Hydrosphere - atmosphere exchanges
Dissolution of atmospheric CO2 in the ocean and degassing of CO2 from the ocean to the atmosphere
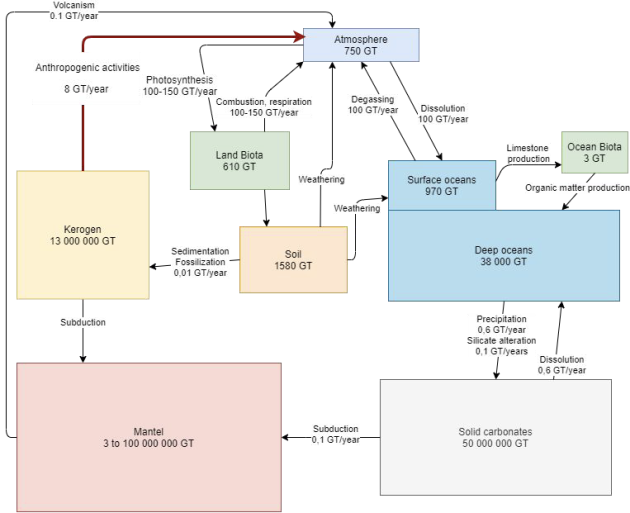
Exchange of 300 GT of CO2 per year ;
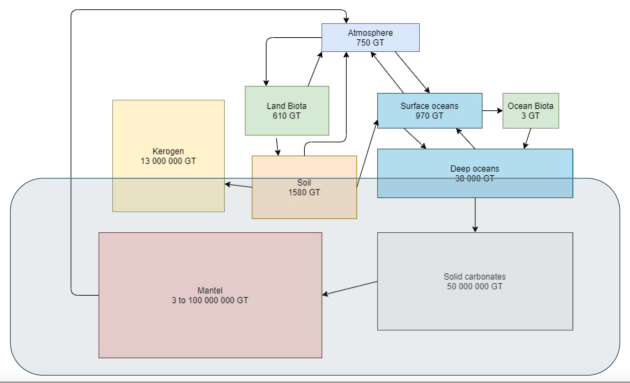
Residence time = quantity of the element in the reservoir / sum of the flows of contribution in the reservoir.
Video to watch :
Henry's Law and Gas Solubility Explained https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9JtTpPEesOk
At constant temperature and saturation, the partial pressure in the vapor phase of a volatile solute is proportional to the mole fraction of that body in the liquid solution.
So the higher the temperature, the less CO2 is soluble, and the more carbon is redistributed to the atmosphere.
For a given amount of carbon in the ocean+atmosphere, the amount of CO2 in the atmosphere increases if the temperature increases.
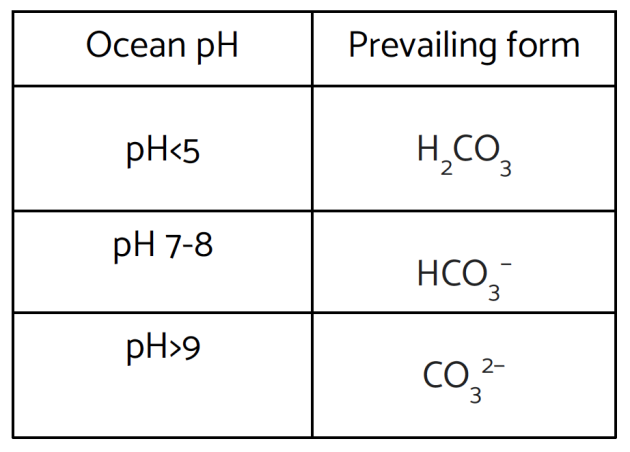
CO2 control : CO2 balance in the hydrosphere
DIC = [CO2(aq)] + [H2CO3] + [HCO3−]+ [CO32−]
Carbon cycle : Short cycle part 2
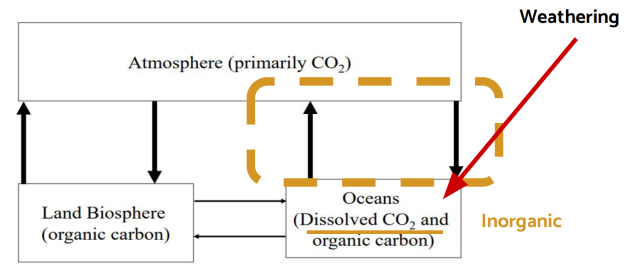
Diversion and leakage in the hydrosphere-atmosphere physical exchanges
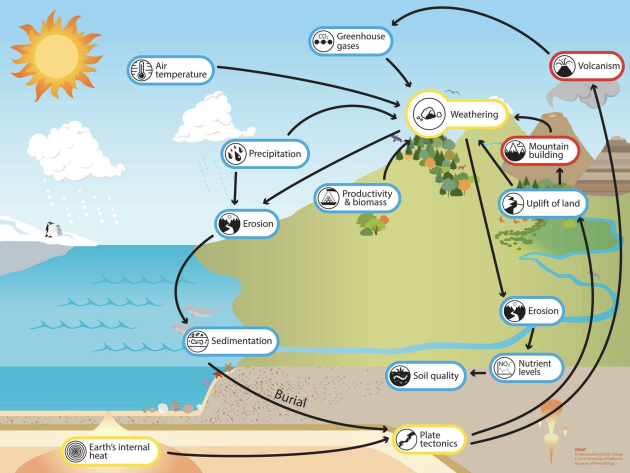
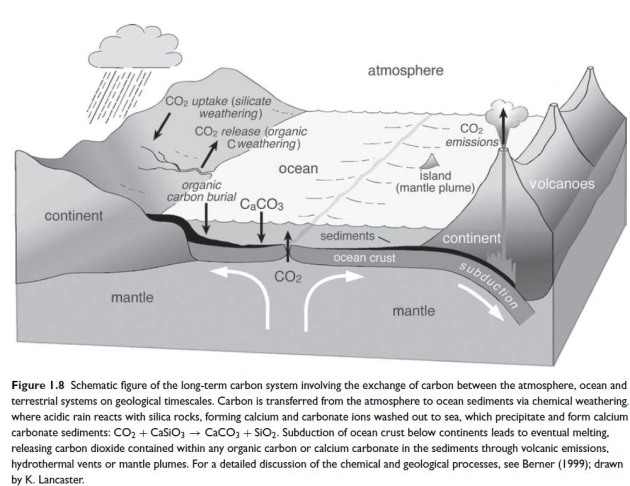
There is a diversion of carbon flux from the atmosphere to the ocean through the weathering of rocks.
To know more about weathering of rocks : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sk B_A2sfBcY
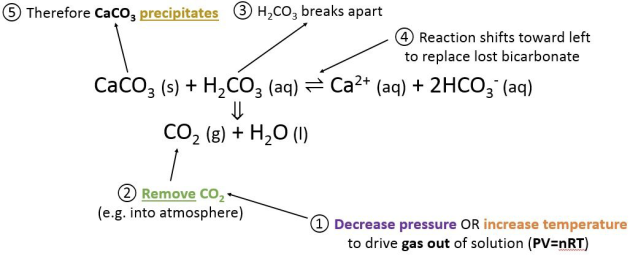
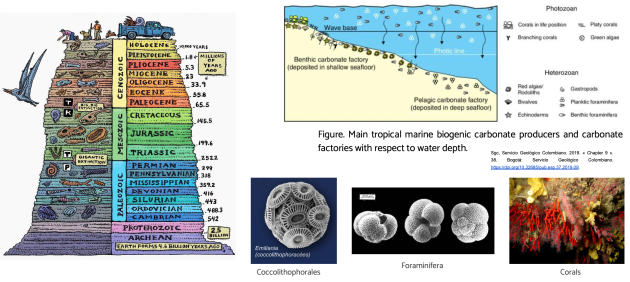
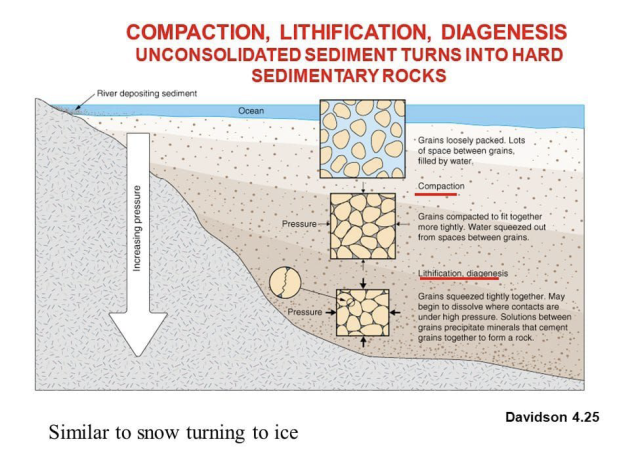
There is a leakage of carbon from the hydrosphere to the lithosphere : the formation of carbonates.
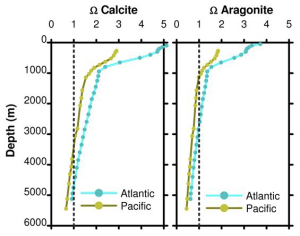
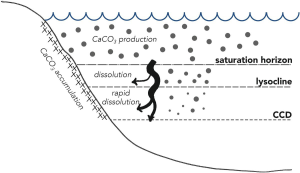
Calcium carbonate solubility
To precipitate calcium carbonate :
Woosley, Ryan J. 2018. « Carbonate Compensation Depth ». In Encyclopedia of Geochemistry, édit par William M. White, 204‑5. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. Cham: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-39312-4_85.
Carbon cycle : Short cycle part 3
Carbon cycle : Short cycle part 4
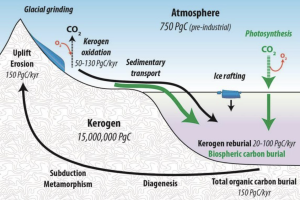
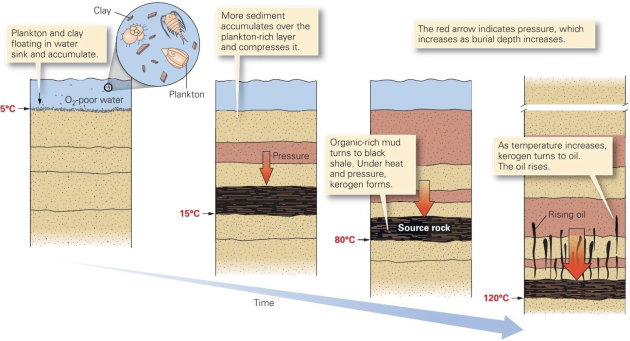
Organic carbon leakage to lithosphere :kerogen formation
Figure : Organic carbon cycle with the flow of kerogen (black solid lines) and the flow of biospheric carbon (green solid lines) showing both the fixation of atmospheric CO2 by terrestrial and marine primary productivity. The combined flux of reworked kerogen and biospheric carbon into ocean sediments constitutes total organic carbon burial entering the endogenous kerogen pool (Galy et al., 2015; Hedges and Oades, 1997).
Conclusion of the short cycle
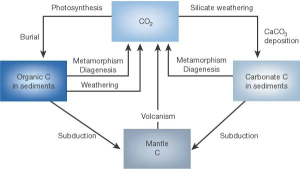
Long cycle
Long carbon cycle
CO2 + CaSiO3 <-> CaCO3 + SiO2
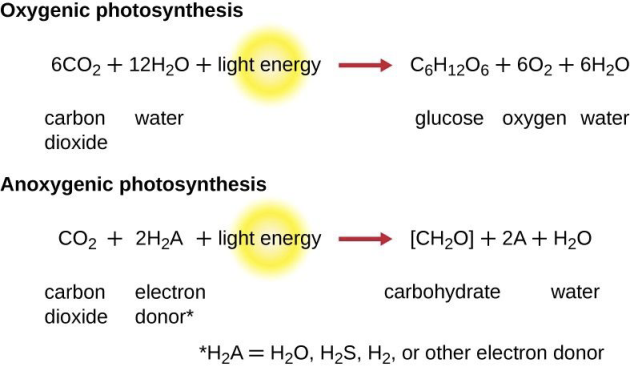
CO2 + H2O <-> CH2O + O2
Berner, Robert A. 2003. « The Long-Term Carbon Cycle, Fossil Fuels and Atmospheric Composition ». Nature 426 (6964): 323‐26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02131.
CO2 + CaSiO3 <->CaCO3 + SiO2
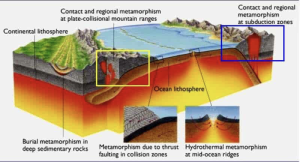
Contact Metamorphism Vs. Regional Metamorphism https://www.geologypage.com/
Trap rock forming a characteristic pavement, Giant's Causeway, Northern Ireland (left)
Three Devil's Grade in mid-Moses Coulee , USA (right)