Anthropogenic activities and carbon cycle
Disruption of the carbon cycle-causes
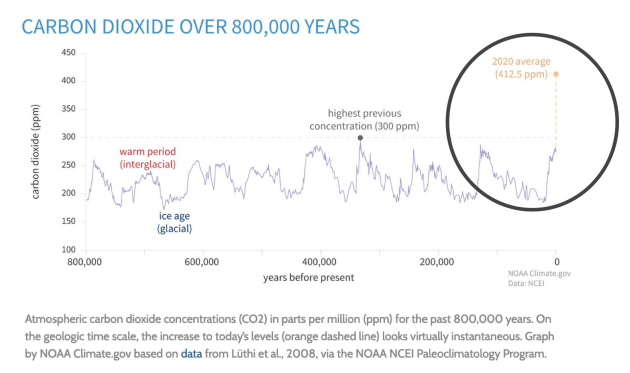
Observation of disruption of the carbon cycle
“Recent increases in global averaged temperature over the last decade already appear to be outside the normal variability of temperature changes for the last thousand years. A number of different analyses strongly suggest that this temperature increase is resulting from the increasing atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases, thus lending credence to the concerns about much larger changes in climate being predicted for the coming decades.” (Wuebbles, 2001)
Source of the disruption
« Human-related emissions from fossil fuel use have been estimated as far back as 1751. Before 1863, emissions did not exceed 0.1 GtC/year. However, by 1995 they had reached 6.5 GtC/year, giving an average emission growth rate slightly greater than 3% per year over the last two and a half centuries. Recent growth rates have been significantly lower, at 1.8% per year between 1970 and 1995. Emissions were initially dominated by coal. Since 1985, liquids have been the main source of emissions despite their lower carbon intensity. The regional pattern of emissions has also changed. Once dominated by Europe and North America, developing nations are providing an increasing share of emissions. »
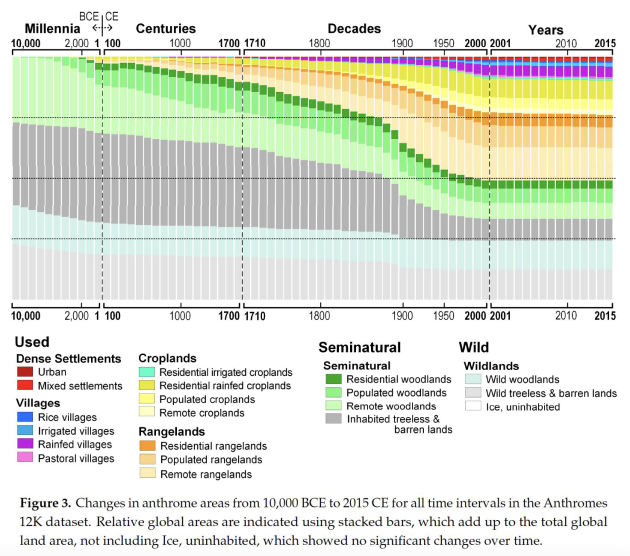
« Physical processes and feedbacks caused by land-use change, that may have an impact on the climate, include changes in albedo and surface roughness, and the exchange between land and atmosphere of water vapour and greenhouse gases [see section 4, chapter 7]. [...] Land-use change may also affect the climate system through biological processes and feedbacks involving the terrestrial vegetation, which may lead to changes in the sources and sinks of carbon in its various forms [see chapter 3)]. »
(IPCC, 2001)
Media
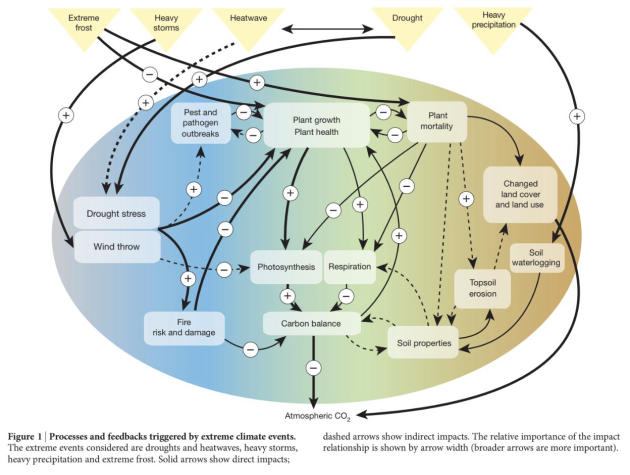
Disruption of the carbon cycle-environmental issues
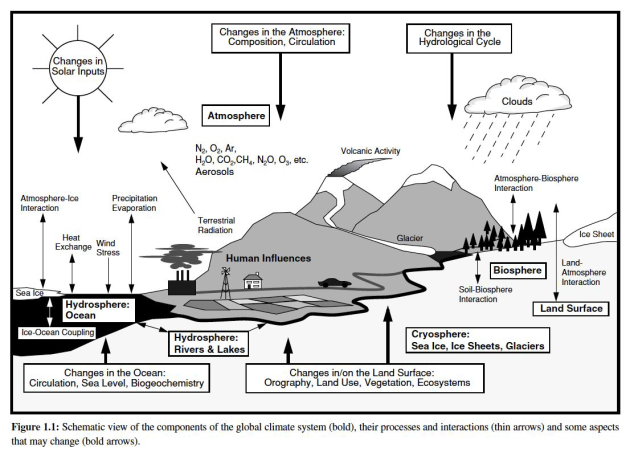
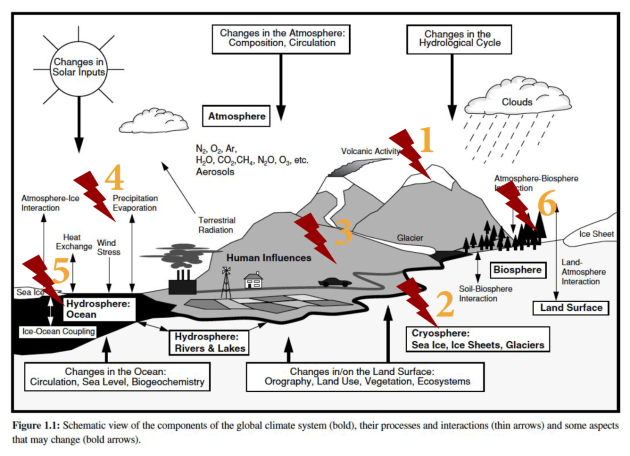
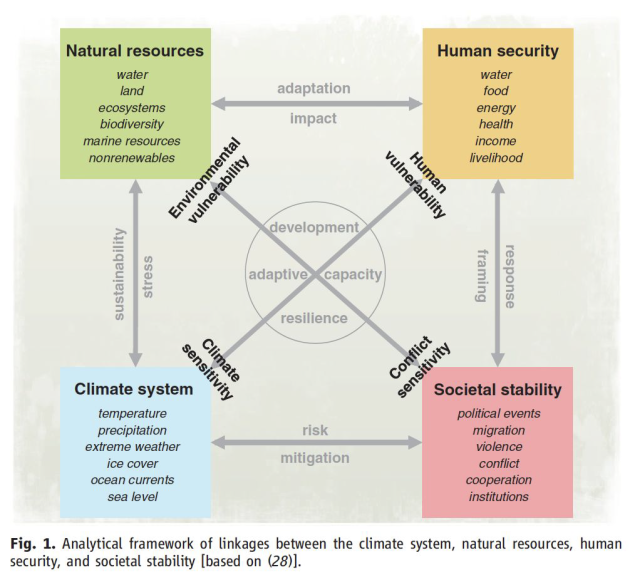
Consequences on the Earth System
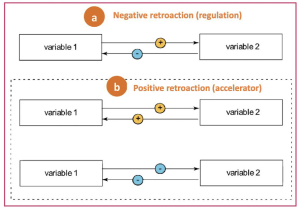
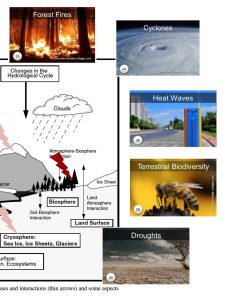
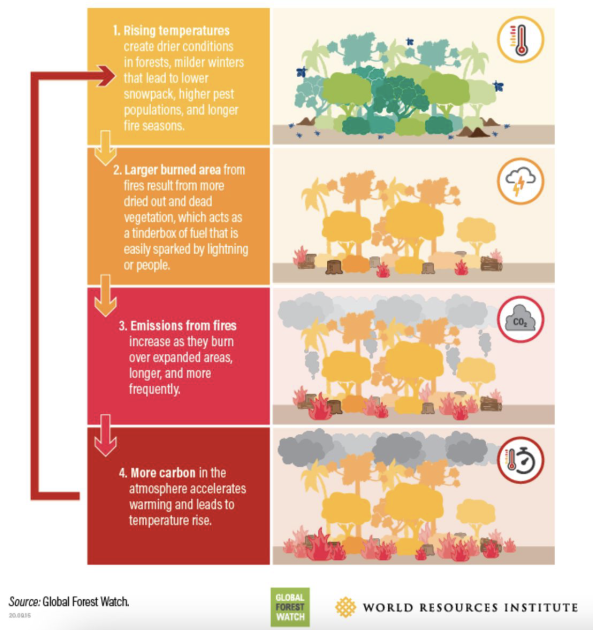
Feedback loops
Feedback loop 6 : focus biodiversity
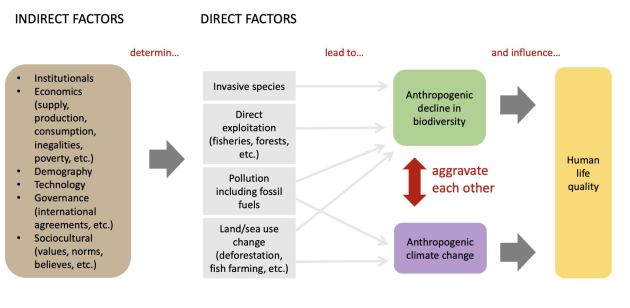
Climate change = main cause of biodiversity loss
Preserving biodiversity = mitigating climate change
/!\ technological solutions to mitigate climate change can have negative impacts on biodiversity
Same causes: our socio-economic way of life
Anthropocene Atlas, Gemenne
Interesting source : https://ipbes.net/sites/default/files/2021-06/20210609_workshop_report_embargo_3pm_CEST_10_june_0.pdf
Media
Disruption of the carbon cycle-social issues
Social impacts
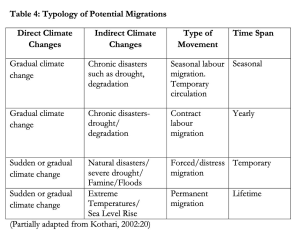
Définition : Climate Refugees
1951 Refugee Convention: refugee = from political persecution (UN)
“Climate Change Displaced People” : people whose habitat is threatened or is already at risk of being extinguished due to climatic change (Hodgkinson et al., 2009)
“Climate refugees” or “forced climate migrants”
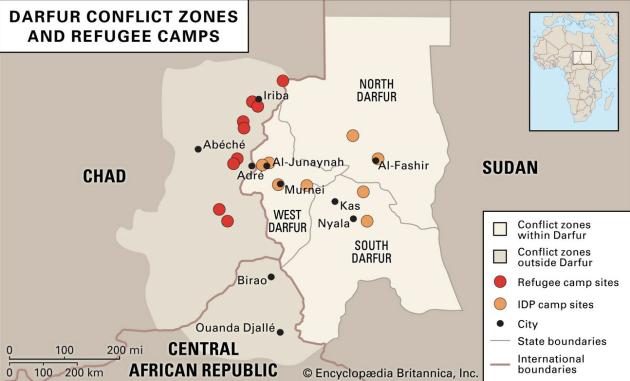
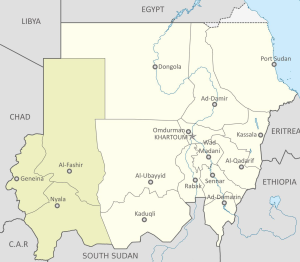
Britannica, The Editors of Encyclopaedia. "Darfur". Encyclopedia Britannica, Invalid Date, https://www.britannica.com/place/Darfur. Accessed 15 September 2021.
The complex ethnic distinctions in Darfur are perhaps less important than the contrast between agriculturalists and pastoralists. The relationship between the two is governed by competition for land and water resources, which can be affected by short- and long-term climate change (whether random, cyclical or greenhouse-induced), both in terms of absolute availability and geographical extent of the resources.
Jeffrey Mazo (2009) Chapter Three : Darfur : The First Modern Climate-ChangeConflict, The Adelphi Papers, 49:409, 73-86, DOI: 10.1080/19445571003755538
Définition : Armed Conflicts
3 elements (Sakaguchi, 2017):
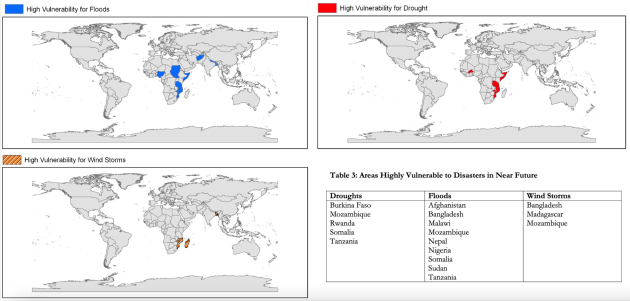
There are correlation between climate change and
violence but no robust conclusion.
There are weak empirical support to the link between climate change and violence
Methodologies used in the different students have an impact on results
« Migration is generally considered to be the intermediate stage which links environmental degradation and disasters to conflict (Homer Dixon, 1991 and 1994) »
(Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Migration and Conflict, Raleigh)