Consomption of abiotic resources
Main threads of the course : Metals and Oil
Metals
Brief global history
Contemporary trends
Oil :
Brief global history
Contemporary trends
Sociotechnical perspective (Tutorial work)
Main threads of the course
The mineral resource example: Metals
Why metals? On the 118 known atoms, most of them are metals :[3]
85 metals
6 metalloids
17 non metals
10 non determined
General properties :
electrical & thermal conductors
mechanical ductility
Geological forms: oxides (common) > sulfides (less common) > natives (uncommon)
The energetical resource example: Oil
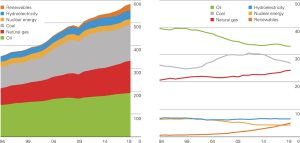
Currently, most used source in main primary energy consomption :
Oil (33,1%)
Coal (27%)
Natural gas (24,2%) [6]
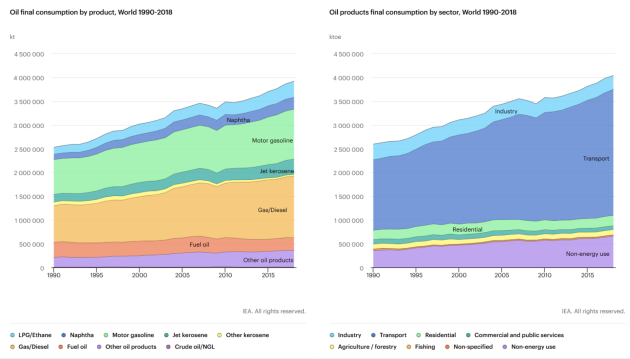
Regroup varied forms of derived fuels (petrol, shale oil) and secondary resources
General properties: gives a lot of secondary resources when refined, good energy density, easy and convenient to transport and to use as energy vector in varied contexts
Metals
Metals global history
A very brief summary [3]
Contrary to first intuition: native metals were the first to be used. Although uncommon (often mixed) they were ealily recognizable:
Copper (at least 8000 BC, and melted since 4000 BC), Gold and Silver (4000 BC)
Alloys starting in 2500 BC with Bronze (Tin & Copper)
Furnaces since at least 1000 BC let reduce oxides (notably, Iron oxide) and developp experiments on alloys (Steel = Iron + Carbon)
Lead, Antimony, Mercury used pure or in allows during Antiquity
This tiny number of metals has constituted the main uses until the XIXth century and structured economical and geopolitical relationships between populations
Besides native platinum in Peru, other metals like Nickel, Zinc, Cobalt have been identified by chemistry and metallurgy (beginning of XVIIIth). And then: Manganese, Molybdenum, Tungsten, Titanium (end of the XVIIIth).
Electrolysis in XIXth allows to separate most elements in pure form, but weak rate of use until the XXth century.
Contemporary trends
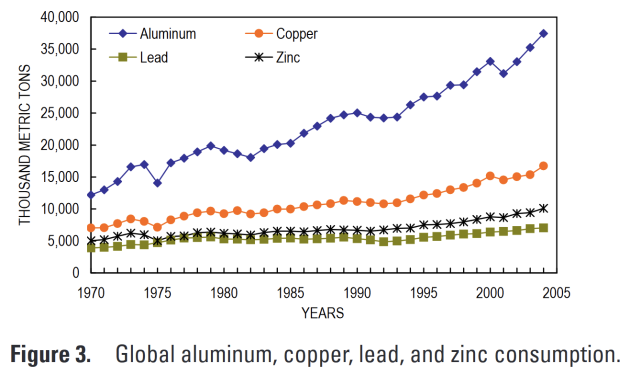
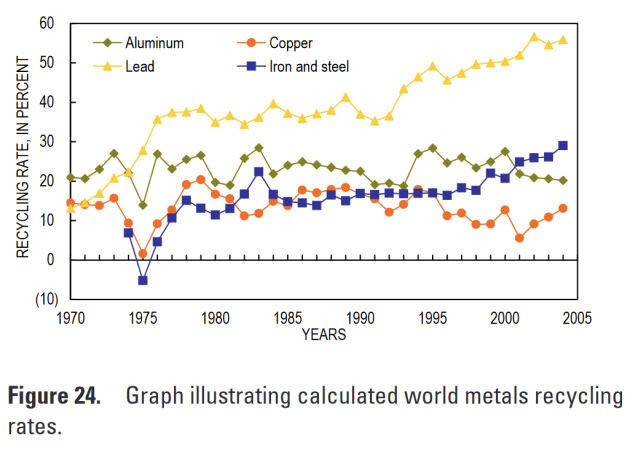
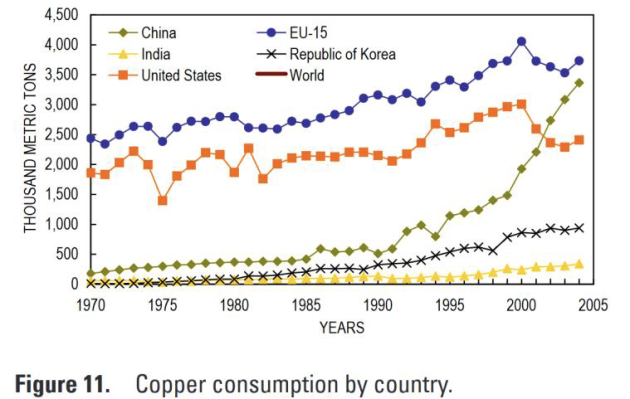
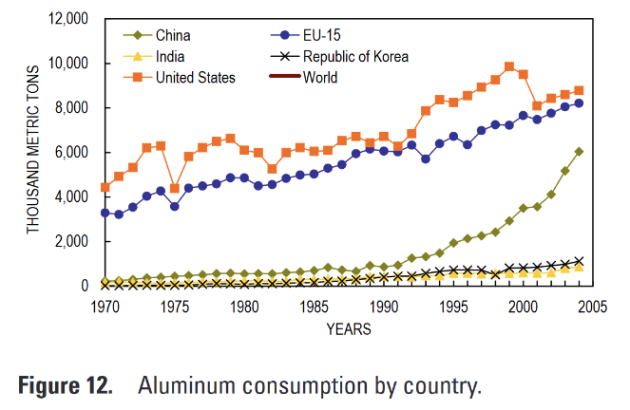
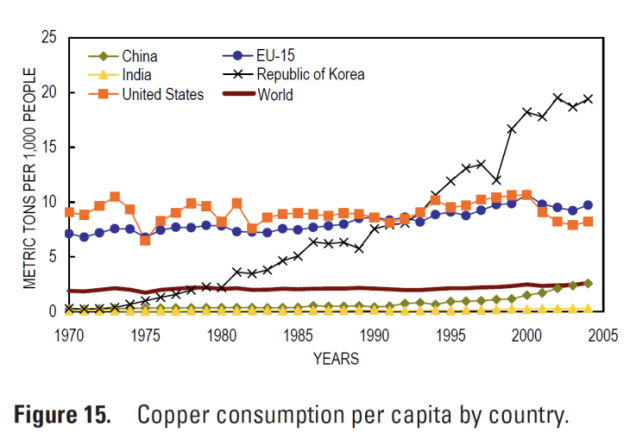
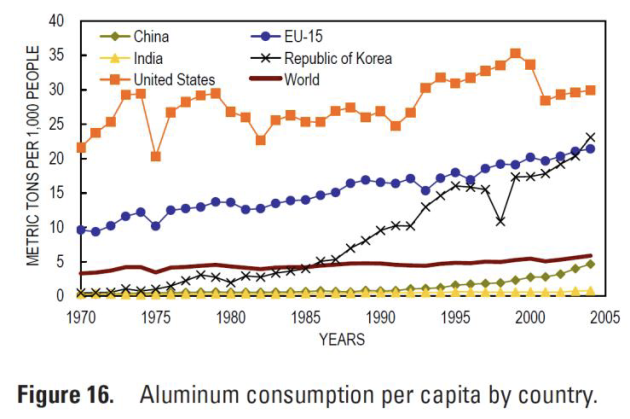
Continuous growth in use of base metals
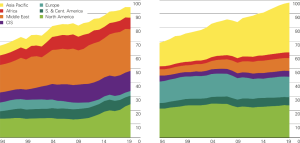
Countries high disparities
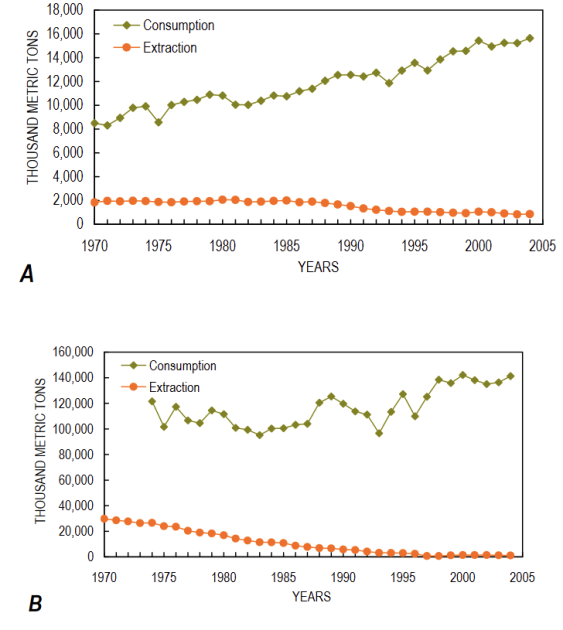
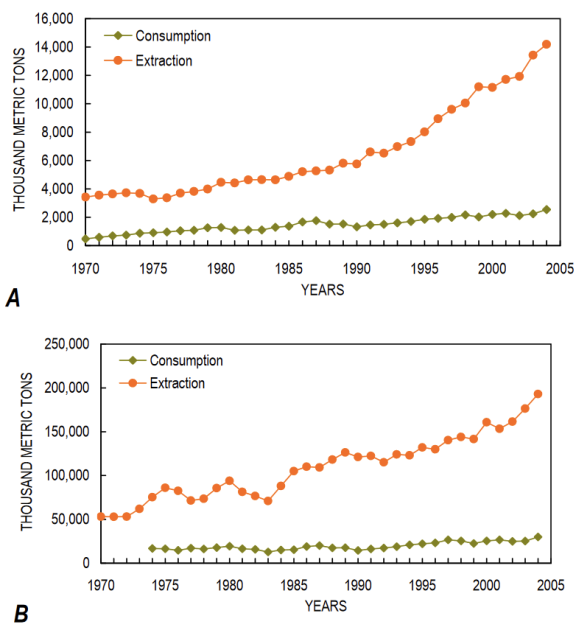
Global Extraction/Consomption pattern
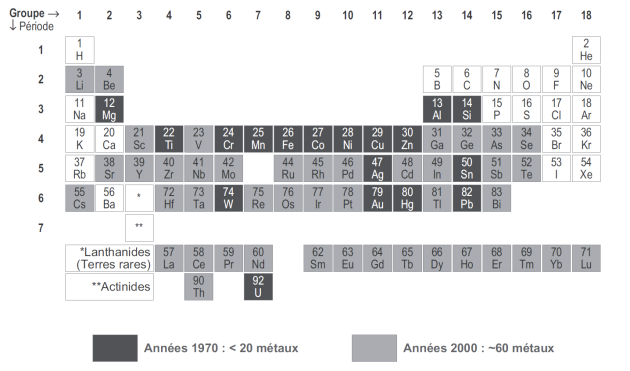
Growing variety of metals for expanding specific uses
Medias
Oil
Oil global history
A very brief summary [8]
Oil has been used for a long time in varied forms
Used as fuel as back as 400 BC in China
Used for lighting or in the asphalt form for construction as back as 2000 BC in Babylon
Crude oil already distilled by Persian chemist in 9th century to obtain tar, used for streets’ paving
Distillation arrive in Europe in 12th century through Islamic Spain
The mid19th –early20th turning point [9]
First industrial oil well and oil refinery around 1850
Consomption stayed low (5% of world energy in 1910), as oil as not that interesting at first, compared to wind or animals for transport, solar& coal were largely dominant for thermal power, etc.
Complex and crossing technical but mostly political phenomena let oil grew in varied uses, to represent more than60% of world energy as soon as 1970
[8] Petroleum, 2020. Wikipedia[online].
[9] BONNEUIL, C., FRESSOZ, J-B, 2016. The Shock of the Anthropocene. The Earth, History and Us.