Management de projets d’éco-innovation
Principes de durabilité - Analyse d’un système
Focus on Human principles
Dans une société durable, les personnes ne sont pas soumises à des barrières systématiques à leur
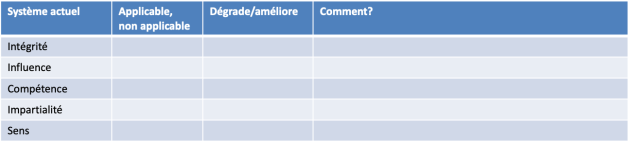
intégrité consiste à ne pas faire subir de préjudice physique, mental ou émotionnel à l’individu.
influence concerne la capacité de l’individu à influencer les systèmes sociaux dont il fait partie et est dépendant.
compétence concerne la possibilité de chacun de se développer et grandir en phase avec ses aptitudes.
impartialité concerne le traitement égalitaire des individus face à d’autres individus ou à des institutions, ce qui équivaut à reconnaitre les mêmes droits et valeurs aux individus.
sens permet de s’assurer qu’il y a une raison pour un individu de faire partie d’une organisation ou d’un système
(Missimier, 2013), (Missimier et Al., 2014)
En quoi mon système actuel dégrade/améliore l’[intégrité, influence, compétence, impartialité, sens] des individus?
Focus on environmental principles
… et dans une société durable, la nature n’est pas soumise à un accroissement systématique
De la concentration de substances extraites de la croûte terrestre (ex. énergies fossiles);
De la concentration de substances produites par la société (ex. GES);
De sa dégradation par des moyens physiques (ex. Étanchéification des sols);
(Holmberg, Robèrt, 2000), (Robèrt et al., 2013)
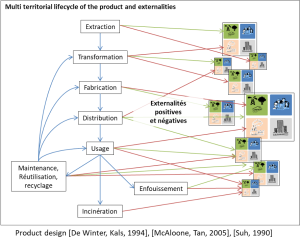
En quoi mon système actuel dégrade/améliore la concentration des substances extraites et produites et ?
Political & territorial principles
Integrity is about not doing direct harm at the individual level - physically, mentally or emotionally.
Influence is about not experiencing barriers to participating in shaping the social system(s) one is part of and dependent on.
Competence is about ensuring that every individual (and group) has the opportunity to develop and grow in line with their skills.
Impartiality is about people being treated equally both between individuals, and between individuals and organizations such as in courts, authorities, etc. It is about acknowledging that all people have the same rights and are of equal worth.
Meaning is about ensuring there is reason for being part of an organization or system: Why should people want to be a part of it?
Principles for sustainable governance (Buclet, 2011)
Participatory Democracy aims to build a balance between individual preferences and common interest in meeting the challenges of sustainable development.
Capability/empowerment aims to maintain and develop the capacity of organizations/individuals to meet their own expectations.
Proximity aims to bring together the decision-making level and the level impacted by the decision.
Competitiveness principle (Allais, 2015): Systematic adoption of intangible capital in both strategic and operational governance.