Toothbrush results interpretation
We only consider two points in this interpretation process : the answer to the main objective and the first investigation on environmental impacts.
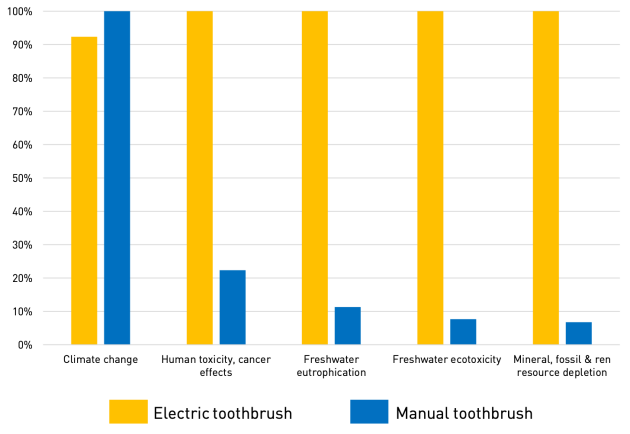
Response to the main objective
Investigation of the impact source
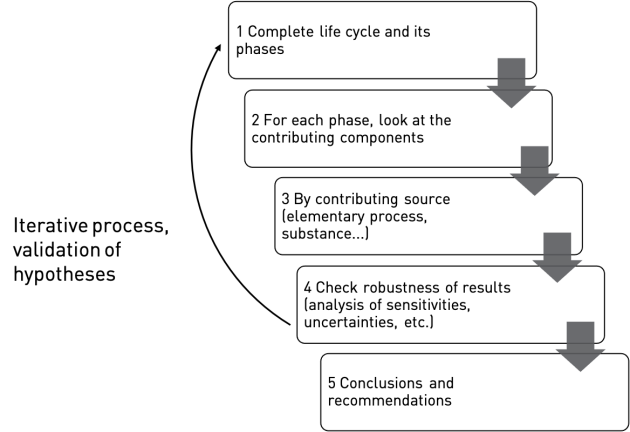
Step-by-step iterative approach
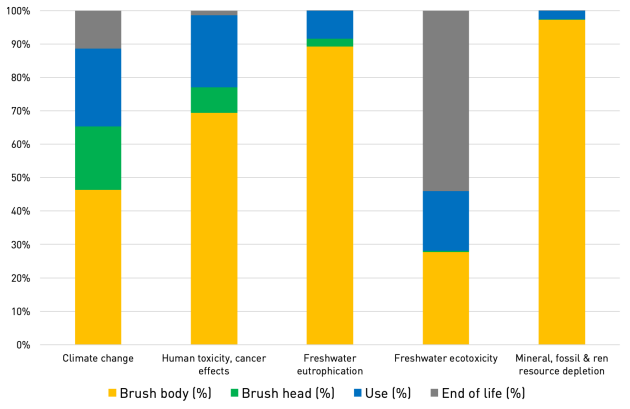
Impacts on the life cycle of an electric toothbrush
The manufacture of the brush is significant in all impact categories. It is even the main source of contribution in four of the five categories (except freshwater ecotoxicity): between 46% and 98%.
The end-of-life phase is a significant contributor (54%) to the freshwater ecotoxicity category.
The use phase, although less impactful, is also significant for three of the five impact categories (around 20-30%).
The ‘Toothbrush’ and ‘Brushhead’ categories cover the materials, manufacturing processes and transport required for each.
Brush body (%) | Brush head (%) | Use (%) | End of life (%) | |
Climate change | 46,30% | 19,04% | 23,23% | 11,43% |
Human toxicity, cancer effects | 69,32% | 7,64% | 21,62% | 1,41% |
Freshwater eutrophication | 89,23% | 2,36% | 8,30% | 0,11% |
Freshwater ecotoxicity | 27,76% | 0,33% | 17,91% | 54,00% |
Mineral, fossil & ren resource depletion | 97,21% | 0,14% | 2,64% | 0,01% |
Sensibility and evaluation of the data quality
The interpretation phase is used to compare the assumptions made throughout the LCA.
It is necessary to assess the quality of the dataset used and the robustness of these assumptions, in particular through sensitivity analyses.